Contact Us
Ultrasound Scan
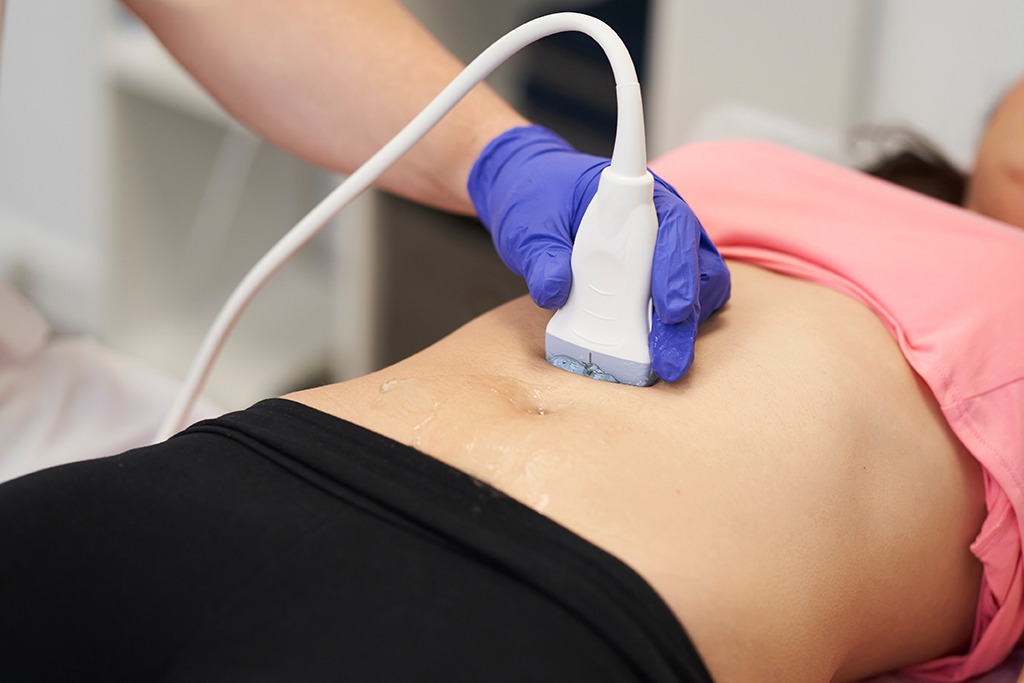
The ultrasound scan is safe, painless and non-invasive. Unlike X-ray and CT scan, ultrasound scan does not utilise ionising radiation. It uses high-frequency sound waves to capture live images of the internal organs of the body. An ultrasound allows your doctor to assess and examine the uterus, pelvis, liver, kidneys and other body organs. Please contact us for the price of the ultrasound scan.
What is an ultrasound scan?
An ultrasound scan is also known as a sonography. It uses high-frequency sound waves to capture live images of the internal organs of the body. It is a non-invasive imaging test that involves the use of a small transducer (the detection tip) and the ultrasound gel applied directly on the skin. The high-frequency sound waves are transmitted from the tip through the gel into the body. When the sound waves bounce off different parts of the body, they create echoes that are collected by the tip and a computer then uses those sound waves to create an image. It can help doctors to diagnose diseases of different organs such as uterine fibroids, endometrioma (chocolate cyst), ovarian cancer, fatty liver, renal failure, heart disease, etc., and examine the foetus in the uterus of pregnant women for the sex, heart, foetal structure and internal organ of the baby. The ultrasound scan is safe, painless and non-invasive. Unlike X-ray and CT scan, ultrasound scan does not utilise ionising radiation. As it captures live images of the body in real-time, it can show the structure and movement of the internal organs, the blood flowing through the vessels, and the foetal movement in the uterus.
Conventional ultrasound displays the images in 2D. Advancements in ultrasound technology include 3D ultrasound that formats the sound wave data into 3D images. Doppler ultrasound is a special technique that allows the radiologist to see and evaluate blood flow through arteries and veins in the abdomen, arms, legs, neck and/or brain (in infants and children) or within various body organs such as the liver or kidneys.
Ultrasound Scan Procedures
Ultrasound examinations are painless and easily tolerated by most patients.
For most ultrasound exams, you will be positioned lying face-up on an examination bed. The doctor will apply a thin layer of gel to the skin. A detector is then placed on your body to send sound waves to your body to produce images. You may be asked to turn to either side to improve the quality of the images. The examination is usually done within 10 minutes.
There is usually no discomfort during the ultrasound scan except for a slight pressure when the tip is pressed against the examined area. Mild discomfort may occur when conducting scans including the insertion of the tip into the body such as transvaginal ultrasound in women and transrectal ultrasound in men.
If a Doppler ultrasound is conducted, you may hear the sound of a pulse that changes as the blood flow is monitored and measured.
You can return to your normal routine after the ultrasound scan.
What are the limitations of ultrasound scans?
The high-frequency sound waves will be blocked by air and therefore cannot be used in screening regarding the stomach, intestines, or organs covered by the intestinal tract. Barium x-ray examination, CT and MRI scans are the preferred methods in this situation.
The high-frequency sound waves also have difficulty penetrating bones (except for the bones of infants which consist of more cartilage). Therefore, other methods such as X-rays, CT or MRI scans are usually adopted to check the internal structure of bones or certain joints.
How do I prepare for an ultrasound scan?
- Ultrasound requires almost no preparation.
- You should wear comfortable, loose-fitting clothing. You may need to remove all clothing and jewellery in the area to be examined.
- For ultrasound of certain body parts, you may be asked to fast 6 hours prior to the test. For a pelvic ultrasound scan, you may be asked to drink six glasses of water before the test, and avoid urination to fill your bladder.
Ultrasound service is available in the following centres:
| Langham Place Flagship Centre (EC Specialists Premium PHF No.: DP000104) L12, Langham Place Office Tower, 8 Argyle Street, Mong Kok (Mong Kok station Exit E1) |
| Argyle Centre 4/F, Argyle Centre Phase1,688Nathan Road, Mong Kok (Mong Kok station Exit D2) 4/F, Argyle Centre Phase1,688Nathan Road, Mong Kok (Mong Kok station Exit D2) |
| Yuen Long Branch Shop No.11-12, Block 2, Yuccie Square, 38 On Ning Road, Yuen Long (Long Ping station Exit E) |
| Tsuen Wan Branch (AmMed Medical Diagnostic Center) Unit 1105, 11/F, CDW Building, 388 Castle Peak Road, Tsuen Wan, N.T. (Tsuen Wan station Exit A3) |
| 銅鑼灣分店 8/F Tower535,535Jaffe Road, Causeway Bay 8/F Tower535,535Jaffe Road, Causeway Bay |
| Central B/F & G/F EC Healthcare Tower (Central), 19-20 Connaught Road Central, Central (Central MTR Exit A1) B/F & G/F EC Healthcare Tower (Central), 19-20 Connaught Road Central, Central (Central MTR Exit A1) |
Ultrasound Scan Q&A
Do ultrasounds use radiation for imaging? Are there any side effects?
The ultrasound scan is safe, painless and non-invasive. Unlike X-ray and CT scan, ultrasound scan does not utilise ionising radiation. Therefore, there are no side effects.
What is the procedure for an ultrasound scan?
Most ultrasound procedures are comfortable and painless. For most ultrasound exams, you will be positioned lying face-up on an examination bed. The doctor will apply a thin layer of gel to the skin. A detector is then placed on your body to send sound waves to your body to produce images. You may be asked to turn to either side to improve the quality of the images. The examination is usually done within 10 minutes.
Which body parts can be examined by ultrasound scan?
Conventional ultrasound displays the images in 2D. Advancements in ultrasound technology include 3D ultrasound that formats the sound wave data into 3D images. Doppler ultrasound is a special technique that allows the radiologist to see and evaluate blood flow through arteries and veins in the abdomen, arms, legs, neck and/or brain (in infants and children) or within various body organs such as the liver or kidneys.
The high-frequency sound waves will be blocked by air and therefore cannot be used in screening regarding the stomach, intestines, or organs covered by the intestinal tract. Barium x-ray examination, CT and MRI scans are the preferred methods in this situation.
The high-frequency sound waves also have difficulty penetrating bones (except for the bones of infants which consist of more cartilage). Therefore, other methods such as X-rays, CT or MRI scans are usually adopted to check the internal structure of bones or certain joints.
Can an ultrasound scan detect heart disease?
A heart ultrasound scan can help doctors to diagnose abnormalities in the structure and function of the heart.
What is the procedure for a pelvic ultrasound?
A pelvic ultrasound consists of abdominal and transvaginal scans. It is painless and easily tolerated by most patients. You will be positioned lying face-up on an examination bed. The doctor will apply a thin layer of gel to the skin. A detector is then placed on your body to send sound waves to your body to produce images. You may be asked to turn to either side to improve the quality of the images. The examination is usually done within 10 minutes. Mild discomfort may occur when conducting scans including the insertion of the tip into the body such as transvaginal ultrasound in women and transrectal ultrasound in men.
Can ultrasound scan detect fatty liver?
An ultrasound scan can detect fatty liver. Fatty liver is usually asymptomatic. However, by examining the liver through an ultrasound scan, doctors can check for any abnormalities in the liver structure for a fatty liver diagnosis.
Are there any situations where an ultrasound scan should not be used?
There are no restrictions on ultrasound scans, and they are suitable for basically everyone.