Bruises on Kids: Why You Should Not Rub Them Hard
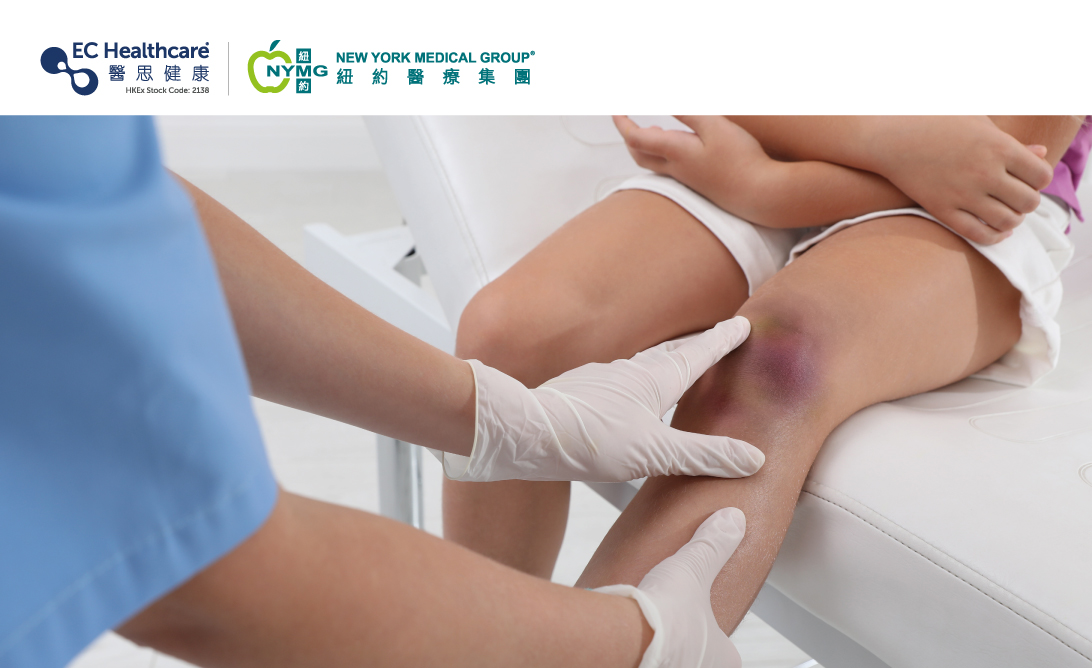

Children are always full of energy and running around, especially when they go outdoors, which can easily lead to scratches and bruises if they are not careful enough. Some parents may overlook these minor bruises and neglect proper treatment, while some may even handle bruises in the wrong way by rubbing them, ending up making things worse.

Handling bruises wrongly can lead to hematomas
Every sport can cause injuries. Common injuries like blunt trauma, contusion, muscle strains and joint sprains can all cause bruises. For example, playing soccer or basketball can lead to injuries from collisions as well as muscle soreness, while cycling can result in falling and lower back pain due to improper posture.
Children can get excited easily and run around during sports, that’s why they often get bruises. However, many parents tend to rub the injured site hard hoping to disperse the bruise, apply hot compresses or rub the site with boiled eggs, but these can actually worsen the local tissue inflammation. Improper treatment of bruises can intensify swelling and inflammation, and even lead to chronic sports injuries. For example, handling a bruise in the wrong way can cause bleeding and swelling under the skin, resulting in a "hematoma". Once a hematoma forms, children may experience long-lasting pain that can restrict mobility over time.
Receive examination if the pain persists
If you spot bruises, swelling or hard lumps on your child during or after exercise, you can follow the four steps R.I.C.E. to relieve your child’s pain:
R (Rest): Stop exercising and rest to avoid moving the injured area.
I (Ice): Apply ice packs to the affected area to help reduce inflammation. Do this three times a day for about 7-8 minutes each time.
C (Compression): Use a special bandage to fix the injured area.
E (Elevation): Elevate the affected area to help promote blood circulation and reduce inflammation.
If your child has a sprain or muscle inflammation that causes foot pain or lower back pain, bring them to a doctor immediately to assess the extent of damage to internal tissues. A detailed examination can help identify the location of displaced joints and injured soft tissues, and facilitate appropriate treatment to avoid further deterioration of the condition.